
Table of contents
**Updates**
We updated this drug summary on 22nd of March 2024, adding simple summary cards, removed TLDR section, and condensed longer paragraphs into summary points to improve readability.

What is cyclizine used for?
Origin of cyclizine
Cyclizine was discovered in 1947. It is chemically made, not from plants or animals.
Cyclizine drug class
Cyclizine is a type of medicine called an antihistamine.
The conditions cyclizine treats
Cyclizine helps with motion sickness, stopping nausea, vomiting, and dizziness. It also treats vertigo (a type of dizziness) that happens after surgery.
Use of cyclizine in palliative (end of life) care
Cyclizine helps with nausea and vomiting caused by bowel blockage, and build up of pressure in the skull.
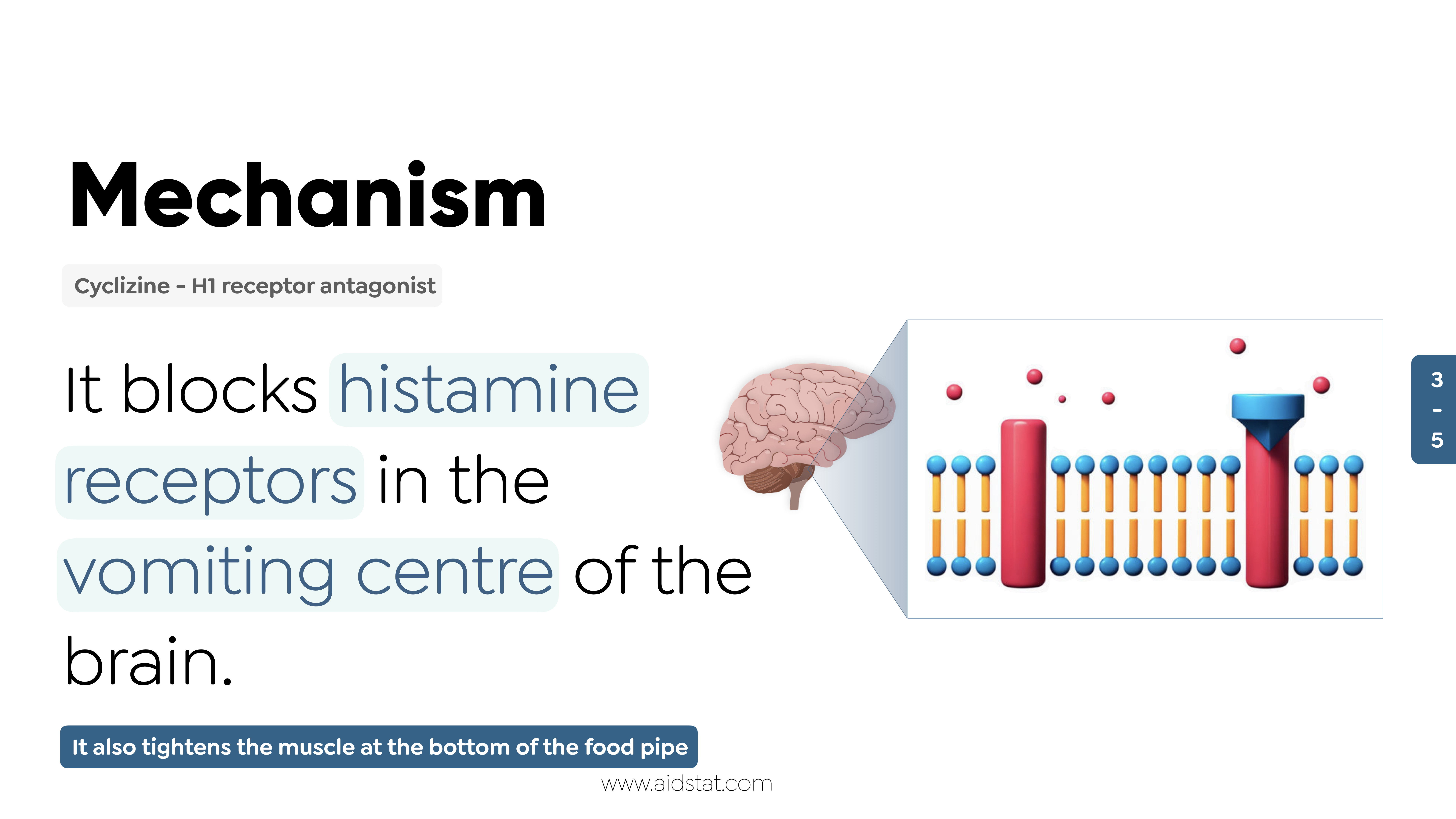
What is the mechanism of action and duration of effect for cyclizine?
Cyclizine helps stop nausea and vomiting by acting as an antihistamine and antiemetic (anti nausea). The exact mechanism is not fully understood yet.
How does cyclizine work in the brain to stop nausea and vomiting?
Cyclizine blocks histamine in the brain, stopping nausea and vomiting signals. It works on H1 receptors found in muscles, blood vessels, and the brain.
How does cyclizine work in the stomach to stop nausea and vomiting?
Cyclizine tightens and makes less sensitive the muscle at the bottom of the food pipe. This helps prevent nausea and vomiting.
What are the anitmuscarinic/anticholinergic properties of cyclizine?
Antihistamines like cyclizine stop acetylcholine, a chemical that attaches to muscarinic receptors in muscles and glands. Blocking it changes heart rate, dries mouth, widens pupils, and more.
When is it best to take cyclizine?
Cyclizine starts working within 20 to 30 minutes to stop nausea and vomiting. It works quickly, so it's best taken before you feel sick or travel. Its effects last for about four hours.
What are the contraindications and Interactions for cyclizine?
Why is cyclizine used with caution in urinary retention?
Cyclizine's anticholinergic effects change the bladder muscle, making emptying harder. This can lead to problems like a stretched bladder or stagnant urine, causing discomfort and infections.
Why is cyclizine used with caution in glaucoma?
Cyclizine widens pupils and raises eye pressure because of its anticholinergic effects. This makes glaucoma worse, where eye fluid doesn't drain properly, causing high eye pressure.
Why is cyclizine used with caution in epilepsy?
Older antihistamines like cyclizine can make seizures easier to happen. For people with epilepsy, this can be risky.
Why is cyclizine used with caution in severe heart failure?
Cyclizine's anticholinergic effects stress the heart. They cause fast and irregular heartbeats, very risky for people with severe heart failure.

Important cyclizine prescribing safety information
Avoid cyczlizine in porphyria
Porphyria is a rare problem with how the body makes heme, which helps blood carry oxygen. Cyclizine is believed to change how heme is made, causing problems for people with porphyria.
Cyclizine negative effects on brain function
Studies show that medicines like cyclizine, with anticholinergic effects, can affect brain function, worsening memory loss, falls in older people, and confusion.
Potential misuse and abuse of cyclizine
There are reports that people can misuse cyclizine to get the effects of hallucinations or euphoria (feelings of happiness).
Dangers of Cyclizine and alcohol
Mixing cyclizine with lots of alcohol is risky because it makes alcohol more harmful.

Cyclizine patient counselling and lifestyle advice
Explain side effects and mechanism of cyclizine
Cyclizine can cause sleepiness, dizziness, dry mouth, blurry eyes, and trouble urinating. These happen because of the antihistamine properties of cyclizine.
Steps to minimise cyclizine side effects
Patients taking cyclizine, should avoid tasks that require focus, like driving, until they know how it affects them. Advise to drink water to stay hydrated and help with dry mouth.
When to seek urgent help
Advise patients to seek urgent medical advice if they experience severe drowsiness, confusion, hallucinations, or convulsions, as these could be serious side effects of the medicine.
Missed dose
Advise patients what to do if a dose is missed. This information can be found in the patient information leaflet.
References
References
1. Brock-Utne, J.G., Rubin, J., Welman, S., Dimopoulos, G.E., Moshal, M.G. and Downing, J.W. (1978). The Action of Commonly Used Antiemetics On The Lower Oesophageal Sphincter. British Journal of Anaesthesia, 50(3), pp.295–298. doi:https://doi.org/10.1093/bja/50.3.295. Link
2. Fares, M.Y., Abdelwahab, N.S., El-Sayed, G.M., Hegazy, M.A. and Abdelrahman, M.M. (2022). Spectrofluorimetric Approach for Quantification of Cyclizine in the Presence of Its Toxic Impurities in Human Plasma; in Silico Study and ADMET Calculations. Journal of Fluorescence, 32(3), pp.993–1003. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-022-02897-3. Link
3. Leach, C. (2019). Nausea and Vomiting in Palliative Care. Clinical Medicine, 19(4), pp.299–301. doi:https://doi.org/10.7861/clinmedicine.19-4-299. Link
4. Sanger, G.J. and Andrews, P.L.R. (2018). A History of Drug Discovery for Treatment of Nausea and Vomiting and the Implications for Future Research. Frontiers in Pharmacology, [online] 9. doi:https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.00913. Link
5. Singh, P., Yoon, S.S. and Kuo, B. (2016). Nausea: a Review of Pathophysiology and Therapeutics. Therapeutic Advances in Gastroenterology, [online] 9(1), pp.98–112. doi:https://doi.org/10.1177/1756283x15618131. Link
6. Vella-Brincat, J.W.A., Begg, E.J., Jensen, B.P., Chin, P.K.L., Roberts, R.L., Fairhall, M., Macleod, S. (A.D.) and Reid, K. (2012). The Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacogenetics of the Antiemetic Cyclizine in Palliative Care Patients. Journal of Pain and Symptom Management, 43(3), pp.540–548. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2011.04.022. Link